Advanced AI technology uncovers vast ancient settlement network hidden beneath dense jungle canopy. The discovery reveals previously unknown connections between ancient civilizations and rewrites our understanding of early urban development. This breakthrough demonstrates the revolutionary potential of AI in archaeological research.
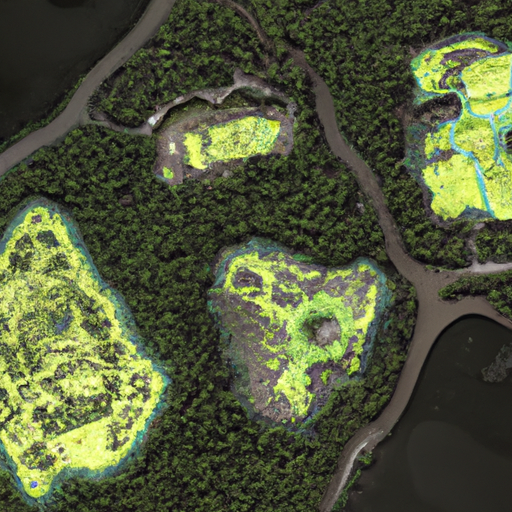
In a remarkable demonstration of artificial intelligence's potential to revolutionize archaeological research, an advanced AI system has discovered an extensive network of ancient settlements hidden beneath dense jungle canopy, fundamentally altering our understanding of early urban civilization. The discovery, made possible through the analysis of complex satellite imagery and LiDAR data, reveals a sophisticated urban network that remained undetected by traditional archaeological methods for centuries.
The AI system, developed through a collaboration between computer scientists and archaeologists, employs deep learning algorithms specifically designed to identify subtle patterns in topographical data that indicate human modification of the landscape. By analyzing vast amounts of data from multiple sources, the system identified thousands of previously unknown structures, roads, and agricultural systems spanning several hundred square kilometers.
What makes this discovery particularly significant is the AI's ability to recognize patterns that human researchers might miss. The system identified subtle relationships between different architectural features and landscape modifications that suggest a level of urban planning and social organization far more sophisticated than previously believed possible for the time period.
The discovered settlement network dates back approximately 1,500 years and appears to have supported a population of several hundred thousand people. The complexity of the urban planning suggests a highly organized society with advanced knowledge of engineering, agriculture, and water management systems.
One of the most striking features of the discovery is an elaborate water management system that includes reservoirs, canals, and flood control structures. This infrastructure demonstrates an impressive understanding of hydraulic engineering and suggests that the civilization had developed sophisticated solutions to manage water resources in a challenging environment.
The archaeological community has been particularly excited by evidence of long-distance trade networks connecting these settlements. The AI system identified what appears to be a complex network of roads and trade routes linking various urban centers, suggesting a level of economic and cultural exchange previously unknown for this region and time period.
The discovery has also yielded insights into the society's agricultural practices. The AI identified extensive agricultural terracing and field systems that indicate advanced farming techniques capable of supporting large urban populations. These findings are forcing researchers to revise their understanding of early agricultural capabilities and population densities in the region.
The technology's success has implications beyond this specific discovery. The AI system's ability to identify subtle archaeological features has opened up new possibilities for archaeological research worldwide. Similar techniques are now being applied to other regions, promising to reveal more hidden ancient settlements and reshape our understanding of human history.
The research team has emphasized that the AI system serves as a tool to augment, rather than replace, traditional archaeological methods. While the technology can identify potential sites of interest, physical excavation and expert analysis remain crucial for understanding the full significance of discoveries.
The project has also demonstrated the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in modern archaeological research. The breakthrough required expertise from various fields, including computer science, archaeology, geology, and environmental science, highlighting how technological innovation can bridge different scientific disciplines.
The discovery has significant implications for our understanding of human civilization's development. The existence of such a large, sophisticated urban network challenges previous assumptions about the capabilities of ancient societies and suggests that complex urban centers developed independently in more places than previously thought.
Researchers are particularly interested in how this civilization managed to sustain such a large population in what is now dense jungle. The findings suggest they had developed advanced techniques for resource management and environmental adaptation that could offer insights relevant to modern challenges of sustainable urban development.
The success of this AI-driven discovery has prompted increased investment in similar technologies for archaeological research. Several institutions have announced plans to develop more sophisticated AI systems specifically designed for archaeological applications, promising even more groundbreaking discoveries in the future.
As the research continues, scientists are using additional technologies, including ground-penetrating radar and advanced dating methods, to build a more complete picture of this ancient civilization. The combination of AI analysis with traditional archaeological methods is creating a new paradigm for understanding human history.
This breakthrough represents not just a significant archaeological discovery but a demonstration of how artificial intelligence can revolutionize our understanding of human history. As these technologies continue to develop, they promise to uncover more hidden chapters in the story of human civilization, helping us better understand our past and, potentially, our future.



